Fred Kubert, Zoltán Kiss- Area Sales Manager - East Europe - Endrich GmbH.
Acoustic I. – Sound generators
8 April 2016

Summary :
Generate a kind of sound is a common requirement in a lot of electronics circuits. All devices, what we call sounders convert electrical energy into mechanical energy that is called acoustic sound energy. It can be used just for signaling some functions with a simple single frequency beep or a certain melody, but could also be neccessary to reproduce human voice or music. For all these purposes the electronic component industry offers many kind of acoustic sound generators.This article is made to give an overview of the different sound sources in order to be able to select the right device for the right purpose. By clarifying some definitions, working principles, and application areas engineers have easier way to understand the product portfolio of the acoustics manufacturers.
1. Signaling devices – Sound generators
When the main purpose of using sound generators is to signal or alert rather than reproduce quality sound or human speech, the wide frequency response is not a requirement. For these applications usually piezo or electromagnetic transducers or buzzers are used. Transducers’ disks are driven from external oscillators (AC signal) while buzzers have built in oscillating electric circuit, only DC voltage needs to be applied to generate sound. The advantage of these simple structured acoustic components is their low current driving, robustness and cost-efficient sound solution.
1.1 Piezo sound generators
The core element in all of the piezo sound generators is a piezoelectric ceramic plate mounted on a metal diaphragm (brass, stainless steel or nickel alloy of a thickness less than 0.5mm).
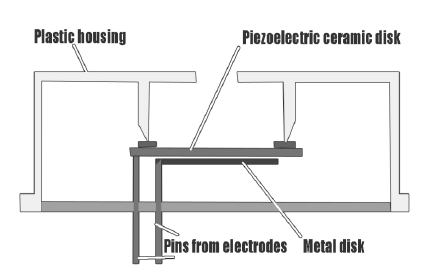
The working principle of the piezo sounders is the physical concept known as the piezoelectric effect. It describes how electricity is generated by applying mechanical stress to piezoelectric crystals, or other way around, how mechanical changes occur by applying AC voltage across the electrodes of the piezoelectric ceramic. According to the frequency of the applied AC voltage the thin piece of piezoelectric ceramic bonded to the metal disk expands and contracts, this vibration produces air pressure waves that human ear considers as sound. The best sound pressure level is achieved when the mechanical resonant frequency matches the frequency of the driving signal. By increasing the voltage up to the maximum allowed on the buzzer both SPL and frequency can be increased, which allows for high sound output. Piezo buzzers use less power, than other sounders. Since they do not need magnetic field for operation, they pose no problems with electromagnetic interference (EMI) or electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). Piezo sounders need low current to drive (few mAmps). They're very high impedance and can be driven directly by a TTL output of the MCU, by using square waves at different rates to make different pitches of beep. A piezo sounder can be also driven by a transistor or any simple oscillator circuit.

Available in a wide variety of sizes, frequencies, and sound outputs, they offer a low cost, high sound output that makes them especially usable for computer devices, telephones, timers, medical devices and toys. Piezo sound generators are the ideal choice for applications which need a simple sound signal within a small frequency range, e. g. warning and control sound signals of household appliances, medical and health care products.
1.2 Piezo speakers
When alert or beep tone is not enough, but there is no need to have an excellent sound quality, just understandable speech or enjoyable sound transmission a smart combination of piezzo sounder and loudspeaker can be used. The piezoelectric speaker consists of a flexible sound supporting plastic diaphragm and a piezoelectric ceramic disc.

This simple structure is capable to provide a wider frequency range than standard piezo sound generators and achieves loud Sound Pressure Levels (SPL). Combined with a well designed housing, SPL over 110 dB at 2 m are possible. This performance makes the piezoelectric speaker the perfect choice for alarm and siren devices. Piezoelectric speakers have several advantages over conventional loudspeakers being resistant to overloads, simple and solid state construction that resists environment (especially water) better than a ribbon or cone based devices. Disadvantage is the frequency response, in most cases, is inferior to that of other technologies, mainly regarding to bass and midrange. This is why they are generally used in applications where volume and high pitch are more important than sound quality.
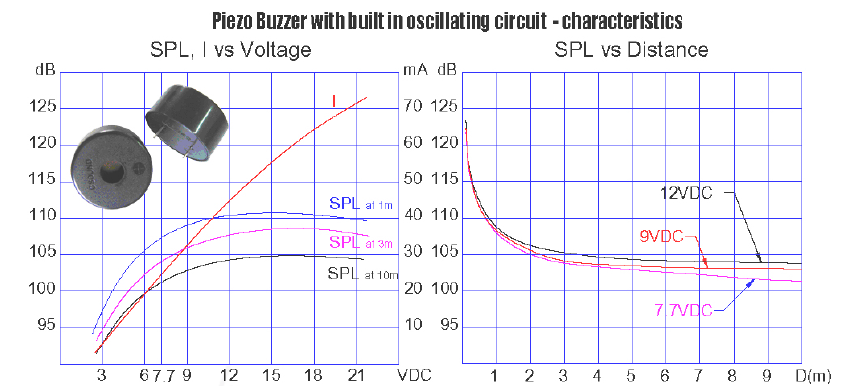
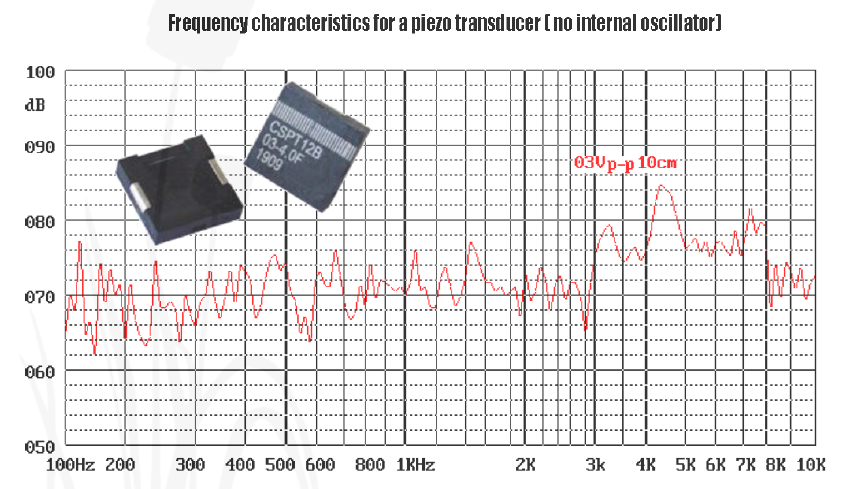
1.3 Electromagnetic sound generators
Electromagnetic sound generators consist of a swinging metal diaphragm driven by an electromagnetic circuit. When voltage is applied to the pins, a magnetic field is created, which causes the magnet to move and the diaphragm to vibrate. When the diaphragm moves, the resulting airwaves produce what the human ear recognizes as sound. These transducers are small and provide a wider frequency range compared with piezoelectric sound generators. They are the right choice for applications, where different frequencies are used to create different sounds. Typical applications are kitchen devices, medical and health care accessories, cellular phones, PDS, etc. In general, electromagnetic sound generators have a higher current consumption than piezo sound generators (100mA range vs. piezo’s 10 mA), due to the generation of electromagnetic energy, but they need lower voltage to achieve their maximum sound pressure level output (2-4V).
2. Dynamic loudspeakers
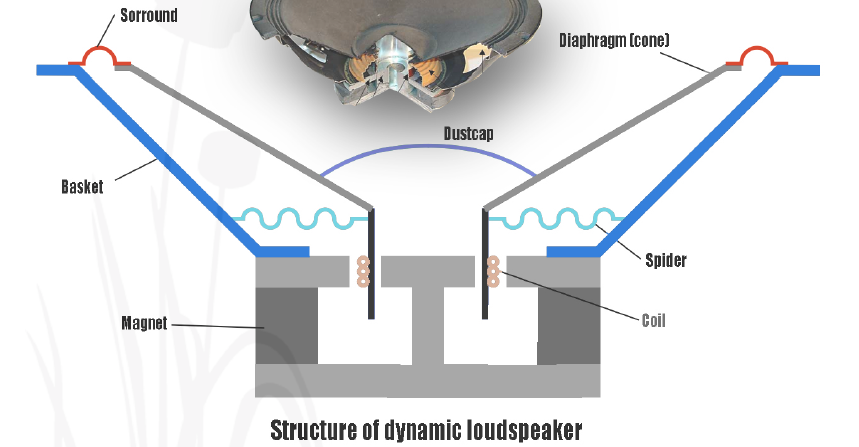
The devices mentioned above are for signaling purposes and not at all capable or limited in voice or music sound reproduction. The universal solution for all higher acoustic wide frequency sound demands is the extensive selection of dynamic loudspeakers. Being high quality speakers or low cost series for sound reproduction in various electronic products, e. g. automotive park distance control/dashboard and alarm sound, cellular phones, telephones, laptops, PDAs, MP3 players, household devices and general electronics, dynamic loudspeakers are the right devices. The dynamic loudspeaker uses a rigid, light, thin paper, plastic or even metal diaphragm, held by a basket via a flexible suspension, which is called a spider (blue waved part on the figure). The voice coil is fixed to this cone, and moves axially through a cylindrical magnetic air gap. When the AC electrical signal is applied to the voice coil, the magnetic field generated by the alternating current turns this construction to an electromagnet. The coil’s magnetic field and the field of the loudspeaker’s permanent magnet interact, generating a mechanical force that causes the coil and the connected diaphragm to move back and forth according to the change of the AC current flowing in the coil. This action moves the air in front of the cone, which generates waves that human ear recognizes as sound. The diaphragm is usually shaped cone- or dome profile, and usually very rigid to only start moving by the electromagnet and not environmental vibrations or other disturbances, should be also very lightweight to have low inertia acting easily to sudden changes of the magnetic field, and should be also damped to reduce vibrations right after the signal is finished. The different diaphragm materials have different properties, usually the above three never meet together. Paper is light and typically well damped, but is not rigid enough, metal is stiff and light, but it usually has poor damping, plastic is usually light, but if it is rigid, then damping properties are weaker.
The suspension system keeps the coil centered in the air gap of the magnet and provides a force that returns the cone to a neutral position after moving. A typical suspension system consists of the spider, which connects the diaphragm and voice coil to the basket, and the surround, which supports this.
Today’s loudspeakers permanent magnets are made of ceramic, ferrite, Alnico (an alloy of Aluminium), or rare earth such as neodymium and samarium cobalt. The design trend requires lighter devices, therefore using rear earth magnets instead of heavier ferrite types is popular. Endrich provides a big variety of dynamic speakers with surface mount, lead, pin and spring terminals with or without custom designed connectors. The product range comprehends several round (ø 15 mm to 57mm) and rectangular shapes (25 mm × 10 mm to 50 mm × 50 mm), which are assembled according to custom design. These loudspeakers are available with impedances from 4 Ω to 150 Ω , rated input power from 0.1 W to 5 W with frequency ranges from 200 Hz to 20 kHz for an operation temperature range of - 40 °C up to + 85 °C (special designs up to + 120 °C).
| Share on Facebook | Share on LinkedIn |
References
This article has been published on the following locations:
| # | Media | Link |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Elektronet 2016/3 | Elektronet : elektronikai informatikai szakfolyóirat, 2016. (25. évf.) 3. sz. 22-24. old. |
| 2 | Elektronet online | Elektronikai eszközökben használt hangkeltők |
| 3 | Hungarian version | Elektronikai eszközökben használt hangkeltők |
| 4 | TechStory M2M | Elektronikai eszközökben használt hangkeltők |
| 5 | South-East European Industrial Market 2016/3 | Acoustic I. – Sound generators in electronic devices |


